Is hair loss a cosmetic problem?
Hair loss is more than just a cosmetic issue; it’s a deeply personal and often distressing experience that can impact your confidence, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. For many men and women between the ages of 30 and 50, the sight of thinning hair or a receding hairline can be a daily source of anxiety. Yet, in a world inundated with quick fixes and miracle cures, the real question remains: Is it possible to stop hair loss?
While most articles on hair loss focus on the symptoms and superficial treatments, few delve into the nuanced and often overlooked aspects that contribute to this condition. The truth is, hair loss is a multifaceted problem influenced by a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Understanding these nuances is crucial if you’re serious about addressing the root causes rather than just treating the symptoms.
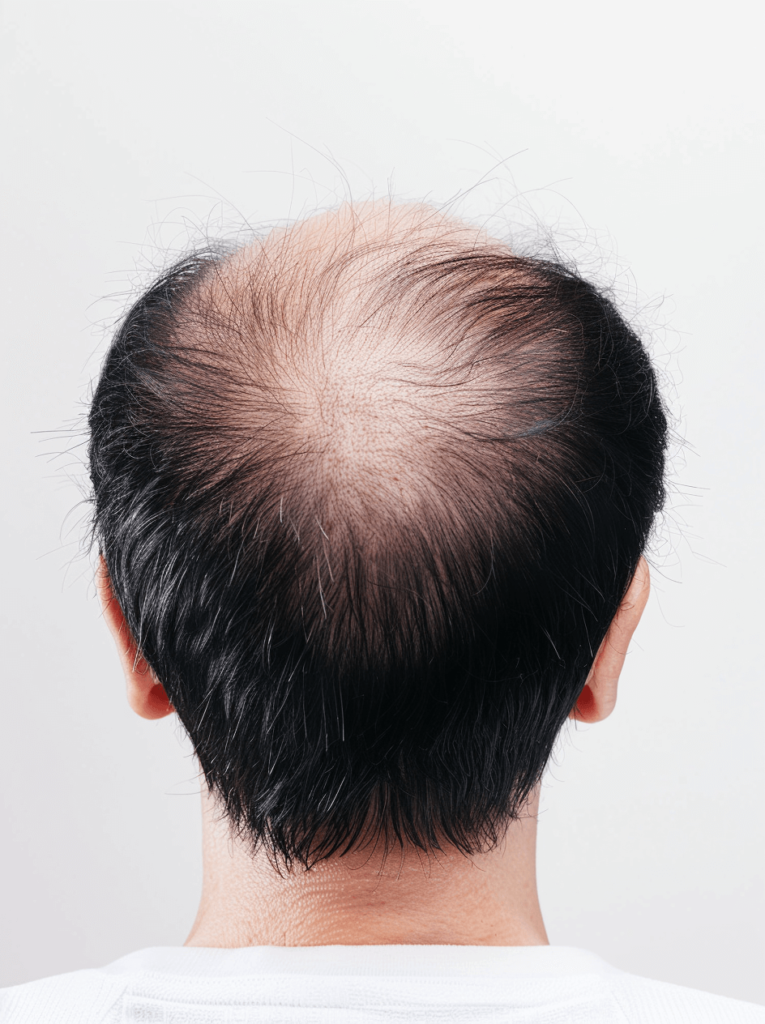
In this article, we’ll explore the lesser-known factors that influence hair loss and shed light on effective, science-backed methods that can help you manage or even reverse this condition. We’ll go beyond the usual advice, offering you a fresh perspective grounded in proven research and real-world experience. Whether you’re dealing with early signs of hair thinning or have been battling hair loss for years, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your hair health.
Understanding Hair Loss
Hair loss is a condition that affects millions of people globally, yet it remains shrouded in misconceptions and incomplete information. To effectively address hair loss, it is essential to first understand the complex mechanisms behind it. Hair loss is not a one-size-fits-all issue; its causes and manifestations can vary widely from person to person. Let’s break down the fundamental aspects of hair loss, including its definitions, causes, and the various types that you may encounter.
What is Hair Loss?
Hair loss, scientifically known as alopecia, is a condition characterized by the reduction of hair density or the complete loss of hair on the scalp and, in some cases, other parts of the body. While it is normal to lose about 50 to 100 hairs daily as part of the natural hair growth cycle, significant hair loss occurs when this cycle is disrupted, and lost hairs are not replaced by new growth. This disruption can be caused by a variety of factors, which we will explore shortly.
What many people don’t realize is that hair loss can be both temporary and permanent. Temporary hair loss, often triggered by stress, hormonal changes, or specific medical conditions, can be reversed if the underlying cause is addressed. Permanent hair loss, however, typically results from genetic factors or irreversible damage to the hair follicles.
Causes of Hair Loss
The causes of hair loss are multifaceted and can be grouped into several key categories:
- Genetic Factors: The most common cause of hair loss is genetics, particularly androgenic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. This hereditary condition leads to gradual hair thinning and is often irreversible without medical intervention.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact hair health. Conditions such as pregnancy, menopause, thyroid dysfunction, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to hair loss. Hormones like dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is derived from testosterone, play a critical role in hair loss, particularly in men.
- Stress and Psychological Factors: Stress is a well-known trigger for hair loss. Conditions like telogen effluvium, where stress pushes hair follicles into a resting phase, can cause sudden and significant hair shedding. Chronic stress can also lead to more permanent forms of hair loss if left unaddressed.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Hair is a reflection of your overall health, and deficiencies in essential nutrients such as iron, protein, vitamins (particularly Vitamin D and B vitamins), and minerals like zinc can lead to hair loss. A diet lacking these critical nutrients can cause hair follicles to weaken and shed prematurely.
- Medical Conditions and Treatments: Various medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata, scalp infections, and chronic illnesses, can contribute to hair loss. Additionally, treatments such as chemotherapy and certain medications for blood pressure, depression, and arthritis are known to cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Hairstyling Practices: Surprisingly, the way you style and treat your hair can also lead to hair loss. Tight hairstyles, frequent use of heat tools, chemical treatments, and harsh hair products can cause traction alopecia and hair breakage, leading to noticeable thinning over time.
Types of Hair Loss
Understanding the type of hair loss you’re experiencing is crucial in determining the best course of action. There are several types of hair loss, each with its unique characteristics:
- Androgenic Alopecia: This is the most common type of hair loss, affecting both men and women. In men, it typically presents as a receding hairline and bald spots, while in women, it often results in overall thinning, especially at the crown.
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to sudden, patchy hair loss. This type of hair loss can occur on the scalp, face, and other parts of the body.
- Telogen Effluvium: This type of hair loss occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting phase simultaneously, often due to physical or emotional stress. The result is widespread thinning across the scalp.
- Anagen Effluvium: Rapid hair loss caused by medical treatments such as chemotherapy. This type of hair loss occurs during the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle and is usually reversible once the treatment ends.
- Traction Alopecia: This form of hair loss is caused by physical damage to the hair follicles, often due to tight hairstyles such as ponytails, braids, or extensions. If detected early, this type of hair loss can be halted and even reversed by changing hairstyling practices.
Can Hair Loss Be Stopped?
The question of whether hair loss can be stopped is one that plagues millions of people as they grapple with the emotional and physical effects of thinning hair. The short answer is: it depends. Hair loss is a complex condition with various causes, and the possibility of halting or reversing it depends on understanding these underlying factors and how early the intervention begins. Let’s explore this in detail to provide a clearer understanding.
Permanent vs. Temporary Hair Loss
One of the first distinctions to make when addressing hair loss is whether it is permanent or temporary. This distinction is crucial because it dictates the strategies available to you for managing the condition.
Permanent Hair Loss: Permanent hair loss is typically genetic and falls under the category of androgenic alopecia, more commonly known as male or female pattern baldness. In these cases, hair follicles shrink over time due to the influence of hormones like dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Once the follicles have shriveled to the point where they can no longer produce hair, the loss is generally irreversible without medical intervention, such as hair transplants or advanced treatments like Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy. This type of hair loss progresses gradually and tends to follow predictable patterns—receding hairlines in men and thinning at the crown in women.
Temporary Hair Loss: On the other hand, temporary hair loss is often the result of external factors such as stress, hormonal imbalances, medical treatments, or nutritional deficiencies. Conditions like telogen effluvium—a stress-induced hair loss—are typically temporary and can often be reversed once the triggering factor is addressed. For instance, hair loss due to pregnancy or postpartum hormonal changes usually resolves itself within months as the body returns to its normal hormonal state. Similarly, hair loss caused by nutrient deficiencies can often be halted and reversed with proper dietary adjustments and supplementation.
Factors Influencing Hair Loss Reversibility
Several factors determine whether hair loss can be stopped or reversed:
1. Early Intervention: The sooner you address the early signs of hair loss, the better your chances of halting its progression. Many people ignore the initial symptoms—thinning at the crown or a widening part—until the hair loss becomes noticeable. However, starting treatment early, particularly for conditions like androgenic alopecia, can significantly slow down or even stop further hair loss. Early intervention allows for a wider range of treatment options, from over-the-counter solutions like Minoxidil to prescription medications like Finasteride.
2. Underlying Health Conditions: The presence of underlying health conditions such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, or chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss. If these conditions are managed effectively, the associated hair loss can often be stopped. For instance, treating hypothyroidism with hormone replacement therapy can restore hormonal balance and reduce hair loss.
3. Treatment Adherence: Consistency in treatment is key to managing hair loss. Whether you’re using topical treatments, taking oral medications, or undergoing procedures like PRP therapy, sticking to the recommended regimen is crucial. Hair growth is a slow process, and visible results often take several months to appear. Discontinuing treatment prematurely can lead to the resumption of hair loss, nullifying the progress made.
4. Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices, including diet, stress management, and hair care practices, play a significant role in hair health. A diet rich in essential nutrients like iron, protein, and vitamins can support hair growth, while stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can mitigate stress-induced hair loss. Additionally, gentle hair care practices, avoiding tight hairstyles, and reducing the use of heat styling tools can prevent further damage and loss.
Realistic Expectations
While many treatments can significantly slow or even stop hair loss, it’s important to set realistic expectations. For those with genetic predispositions, such as male or female pattern baldness, completely stopping hair loss may not be possible without ongoing treatment. In these cases, the goal is often to slow the progression and preserve as much hair as possible rather than achieving complete regrowth.
Moreover, while temporary hair loss can often be reversed, it requires patience and consistency. Hair regrowth takes time, and improvements may not be visible for several months. Understanding this timeline and maintaining a long-term commitment to treatment is essential for success.
Effective Treatments for Hair Loss
When it comes to hair loss, the search for effective treatments can be overwhelming. The market is flooded with products and procedures claiming to restore your hair to its former glory. However, not all treatments are created equal, and it’s crucial to separate fact from fiction. In this section, we’ll explore the most effective, scientifically-backed treatments for hair loss, providing you with the information needed to make informed decisions about your hair care regimen.
Over-the-Counter Medications
One of the most accessible and widely used treatments for hair loss is Minoxidil, commonly known by the brand name Rogaine. Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical solution available in liquid or foam form. It’s applied directly to the scalp and works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles, prolonging the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle. This increased circulation helps to revitalize shrunken hair follicles, leading to thicker and longer hair over time.
Minoxidil is particularly effective for treating androgenic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness) and has been shown to slow down hair loss and promote regrowth in many users. However, it’s important to note that results vary from person to person, and continuous use is required to maintain the benefits. Discontinuing Minoxidil often leads to a return of hair loss.
Prescription Medications
For those seeking a more potent solution, Finasteride (Propecia) is a prescription medication that has been proven to be highly effective in treating male pattern baldness. Finasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles in androgenic alopecia, leading to thinning hair and eventual hair loss.
By lowering DHT levels, Finasteride can halt the progression of hair loss and, in some cases, even promote regrowth. Clinical studies have shown that Finasteride can reduce hair loss in up to 90% of men and stimulate new hair growth in about two-thirds of users. However, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects, including a decreased libido and erectile dysfunction, which are experienced by a small percentage of users. Women, especially those who are pregnant or may become pregnant, should avoid Finasteride due to the risk of birth defects.
Medical Procedures
When medications are not sufficient or for those looking for more dramatic results, medical procedures such as hair transplants and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy offer promising options.
Hair Transplants: Hair transplant surgery is a well-established method for treating hair loss, particularly in cases of advanced androgenic alopecia. The procedure involves harvesting hair follicles from areas of the scalp where hair is more abundant (usually the back or sides) and transplanting them to areas with thinning or no hair. The transplanted hair follicles are typically resistant to DHT, meaning they are less likely to fall out over time.
There are two main types of hair transplant procedures: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). FUT involves removing a strip of scalp and dissecting it into individual follicular units, while FUE involves extracting individual follicles directly from the donor area. Both methods have high success rates, but FUE is generally preferred due to less scarring and a faster recovery time.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy is an innovative treatment that has gained popularity in recent years. The process involves drawing a small amount of your blood, spinning it in a centrifuge to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting this platelet-rich plasma into your scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
Studies have shown that PRP therapy can increase hair density, thickness, and overall scalp health. It’s particularly effective when used in conjunction with other treatments like Minoxidil or hair transplants. PRP is generally considered safe, as it uses your body’s own cells, reducing the risk of allergic reactions or side effects. However, multiple sessions are usually required, and the cost can add up over time.
Emerging Treatments
In addition to established treatments, several emerging therapies show promise in combating hair loss. One such treatment is Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), which uses red light or near-infrared light to stimulate hair follicles and increase hair density. LLLT is thought to work by improving cellular respiration and energy production within the hair follicles, leading to stronger and healthier hair. Devices for LLLT, such as laser caps or combs, are available for home use, though consistency and patience are required to see results.
Another emerging treatment is topical phenylephrine, which is still in the research phase. Phenylephrine is believed to stimulate the tiny muscles in hair follicles that control hair shaft contraction, making hair less likely to be pulled out during styling or brushing. While this treatment is not yet widely available, early studies suggest it could be a valuable addition to the hair loss treatment arsenal in the future.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Hair Loss
While medical treatments and procedures can play a significant role in managing hair loss, lifestyle changes are equally important in preventing and mitigating hair thinning and shedding. A holistic approach that includes adjustments to your daily habits can not only help slow down hair loss but also improve the overall health and vitality of your hair. In this section, we will explore key lifestyle changes that can contribute to healthier, stronger hair and potentially prevent hair loss.
Dietary Adjustments
Your diet has a profound impact on the health of your hair. Hair follicles are among the most metabolically active cells in the body, and their growth can be influenced by the nutrients you consume. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins is essential for maintaining healthy hair and preventing hair loss.
1. Protein-Rich Diet: Hair is primarily made up of a protein called keratin. Therefore, consuming an adequate amount of protein is crucial for hair growth and strength. A diet lacking in protein can lead to hair thinning and loss. Incorporate high-quality protein sources such as eggs, fish, lean meats, beans, and nuts into your meals. For those following a vegetarian or vegan diet, tofu, lentils, quinoa, and legumes are excellent protein-rich options.
2. Essential Vitamins and Minerals: Several vitamins and minerals play vital roles in hair health. For instance, Vitamin D is important for follicle cycling, and a deficiency can lead to hair thinning. Similarly, iron is critical for oxygenating your hair follicles, and a lack of it can cause anemia-related hair loss. Other key nutrients include Vitamin A, B-vitamins (particularly Biotin), Vitamin C, and zinc. To ensure you’re getting these nutrients, focus on a varied diet that includes leafy greens, fruits, whole grains, and fortified foods.
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids found in foods like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. They can help maintain a healthy scalp environment and prevent conditions like dry scalp or inflammation that can contribute to hair loss.
Stress Management
Stress is a well-known trigger for several types of hair loss, including telogen effluvium and alopecia areata. Managing stress effectively can help prevent these conditions and promote overall hair health.
1. Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness techniques and meditation can significantly reduce stress levels. These practices help calm the mind, reduce anxiety, and improve mental well-being, which in turn can prevent stress-induced hair loss. Dedicating just 10-15 minutes a day to mindfulness exercises or deep breathing can make a significant difference.
2. Physical Activity: Regular physical activity is not only good for your overall health but also for your hair. Exercise improves blood circulation, including to the scalp, which nourishes hair follicles and promotes healthy hair growth. Activities like yoga, swimming, walking, or even dancing can be effective stress-busters.
3. Sleep Hygiene: Quality sleep is essential for the body’s repair and regeneration processes, including hair growth. Poor sleep or sleep deprivation can exacerbate stress and disrupt hormone levels, leading to hair loss. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night and establish a relaxing bedtime routine to improve your sleep quality.
Hair Care Practices
How you care for your hair on a daily basis can greatly influence its strength, resilience, and overall health. Gentle hair care practices can prevent unnecessary damage and reduce the risk of hair loss.
1. Avoiding Tight Hairstyles: Hairstyles that pull tightly on the hair, such as ponytails, braids, or buns, can cause traction alopecia, a type of hair loss resulting from excessive tension on the hair shaft. If you frequently wear your hair in tight styles, consider switching to looser hairstyles that don’t strain your hair follicles.
2. Minimize Heat Styling: Frequent use of heat styling tools like blow dryers, straighteners, and curling irons can weaken the hair shaft and lead to breakage. Whenever possible, allow your hair to air dry naturally and limit the use of heat tools. If you must use them, apply a heat protectant spray to minimize damage.
3. Choose Gentle Hair Products: The products you use on your hair can either support or undermine its health. Harsh shampoos, conditioners, and styling products can strip your hair of natural oils, leading to dryness and breakage. Opt for sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners that are formulated for your specific hair type. Additionally, consider incorporating a leave-in conditioner or hair serum to add moisture and protect your hair throughout the day.
4. Regular Scalp Care: A healthy scalp is the foundation for healthy hair. Regularly cleansing your scalp to remove excess oil, dirt, and product buildup is crucial. Massaging the scalp during washing can also stimulate blood circulation, encouraging hair growth. Consider using a clarifying shampoo once a month to thoroughly cleanse the scalp and prevent clogged hair follicles.
The Role of Supplements in Hair Health
In the quest for healthy, voluminous hair, many individuals turn to supplements as a potential solution to prevent or combat hair loss. The idea is simple: if the body lacks certain nutrients essential for hair growth, supplementing those nutrients should, in theory, help improve hair health. While the efficacy of supplements can vary depending on the individual and the specific hair loss condition, there is scientific evidence to support the role of certain vitamins and minerals in promoting hair growth and maintaining overall hair health. In this section, we’ll explore the most important supplements that have been shown to support hair health and discuss their potential benefits and limitations.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Hair growth is a complex biological process that requires a variety of nutrients to function optimally. Here are some of the most important vitamins and minerals known to play a critical role in hair health, which you can find in hair loss supplements and appropriate food products:
1. Biotin (Vitamin B7):
Biotin, also known as Vitamin B7 or Vitamin H, is one of the most well-known supplements for hair health. It plays a key role in the production of keratin, a protein that makes up the structure of hair, skin, and nails. Biotin deficiency can lead to hair thinning and loss, making supplementation beneficial for those with low levels of this vitamin. While biotin is available in various foods such as eggs, nuts, and seeds, some people may require additional supplementation, especially if they experience noticeable hair thinning. However, it’s important to note that taking biotin supplements may only be effective for individuals who are deficient in this nutrient.
2. Vitamin D:
Vitamin D is crucial for the health of hair follicles, which are the tiny pores from which hair grows. A deficiency in Vitamin D has been linked to various forms of hair loss, including alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that causes patchy hair loss. The body synthesizes Vitamin D when the skin is exposed to sunlight, but for those who have limited sun exposure or live in areas with long winters, supplementation may be necessary. Vitamin D supplements are widely available and can help restore adequate levels, potentially improving hair growth and preventing further loss.
3. Iron:
Iron is essential for the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body’s tissues, including the hair follicles. Iron deficiency, particularly in women, is a common cause of hair loss. This condition, known as iron deficiency anemia, can lead to diffuse hair thinning across the scalp. Increasing iron intake through diet or supplements can help replenish iron stores and support healthy hair growth. Iron-rich foods include red meat, spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals, but in cases of significant deficiency, iron supplements may be required under medical supervision.
4. Zinc:
Zinc is a trace mineral that plays an important role in hair tissue growth and repair. It helps keep the oil glands around the follicles functioning properly, which is essential for maintaining a healthy scalp environment. Zinc deficiency is relatively uncommon but can lead to hair loss and other issues such as a flaky scalp. While zinc is available in foods like shellfish, beef, and pumpkin seeds, supplementation may be necessary for individuals with absorption issues or higher nutritional needs. However, it’s important to avoid excessive zinc intake, as too much zinc can actually lead to hair loss.
5. Vitamin E:
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells, including hair follicles, from oxidative stress caused by free radicals. It also improves blood circulation, which can enhance nutrient delivery to the scalp and hair follicles. Some studies have shown that Vitamin E supplementation can improve hair growth in individuals with certain types of hair loss. Foods rich in Vitamin E include nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables, but supplementation can provide an added boost for those needing extra support.
Popular Hair Growth Supplements
In addition to individual vitamins and minerals, there are several proprietary hair growth supplements that combine multiple nutrients to target hair health more comprehensively. Some of the most popular and widely used hair growth supplements include:
One of the best supplements that we consider effective in combating hair loss, Folicerin, we have already described on our website. However, in order to provide our readers with broader knowledge, we did some research and checked similar products.
1. Nutrafol:
Nutrafol is a popular hair supplement that contains a blend of vitamins, minerals, and botanical ingredients designed to support hair growth and reduce hair thinning. The formula includes biotin, Vitamin D, zinc, saw palmetto (a plant extract that may block DHT, a hormone linked to hair loss), and ashwagandha (an adaptogen that helps reduce stress, which can contribute to hair loss). Nutrafol is available in different formulations for men and women, catering to specific hormonal and environmental factors that can affect hair health.
2. Viviscal:
Viviscal is another well-known hair supplement that has been clinically tested for its efficacy in promoting hair growth. It contains a proprietary marine complex called AminoMar, along with biotin, Vitamin C, and zinc. Viviscal is particularly popular among individuals experiencing thinning hair, and it has been shown to improve hair thickness and reduce shedding when taken consistently over several months.
3. Hairfinity:
Hairfinity supplements are formulated with a blend of biotin, silica, and other essential nutrients that support hair strength and growth. The product also includes a capilsana complex, which is a blend of hydrolyzed collagen, MSM, and horsetail extract, all of which are believed to enhance hair health. Hairfinity is designed to improve hair elasticity, reduce breakage, and promote longer, stronger hair.
Effectiveness and Considerations
While many individuals report positive results from taking hair growth supplements, it’s important to approach them with realistic expectations. Supplements can support hair health and may prevent further hair loss, but they are not a miracle cure, especially for genetic conditions like androgenic alopecia. The effectiveness of supplements can vary based on individual factors such as genetics, underlying health conditions, and the specific cause of hair loss.
Moreover, before starting any supplement regimen, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider. Some vitamins and minerals can interact with medications or cause adverse effects if taken in excessive amounts. For instance, high doses of Vitamin A or zinc can lead to toxicity and actually contribute to hair loss, rather than preventing it.
Psychological Impact of Hair Loss
Hair loss is not just a physical condition; it is deeply intertwined with one’s psychological and emotional well-being. For many, hair is more than just a collection of strands; it represents identity, youth, vitality, and attractiveness. As a result, the experience of losing hair can be profoundly distressing, affecting self-esteem, confidence, and mental health. In this section, we will explore the psychological impact of hair loss and discuss strategies for coping with the emotional challenges it presents.
The Emotional Toll of Hair Loss
Hair loss can trigger a range of emotional responses, from mild anxiety to severe depression. For both men and women, hair is often a significant part of their self-image. The sudden or gradual loss of hair can lead to feelings of helplessness and loss of control, especially when hair loss is perceived as irreversible or as a sign of aging.

1. Loss of Self-Esteem:
One of the most immediate impacts of hair loss is a decline in self-esteem. Many people associate a full head of hair with beauty, youth, and health. When hair begins to thin or fall out, individuals may feel less attractive, leading to a negative self-image. This can be particularly challenging in social situations where appearance is often emphasized, such as in the workplace or on social media.
2. Anxiety and Stress:
The fear of losing more hair or becoming completely bald can create significant anxiety. This anxiety may be exacerbated by societal pressures and beauty standards that equate hair with femininity or masculinity. For some, the anxiety surrounding hair loss can become all-consuming, leading to avoidance of social interactions and a decrease in overall quality of life. Additionally, the stress of dealing with hair loss can create a vicious cycle, as stress itself can contribute to further hair shedding.
3. Depression:
In more severe cases, hair loss can lead to depression, particularly if the individual feels that they have lost an essential part of their identity. This is often seen in people who experience sudden or severe hair loss, such as those undergoing chemotherapy. The emotional pain of losing hair can be as debilitating as the physical symptoms, leading to a sense of hopelessness and despair. Depression related to hair loss can manifest in various ways, including withdrawal from social activities, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and a lack of interest in previously enjoyed activities.
Social and Relationship Impacts
Hair loss can also affect personal relationships and social interactions. Many people feel embarrassed or self-conscious about their appearance, leading them to withdraw from social situations or avoid activities they once enjoyed. This withdrawal can strain relationships with friends, family, and romantic partners.
1. Social Withdrawal:
Individuals experiencing hair loss may begin to isolate themselves to avoid potential judgment or comments about their appearance. This social withdrawal can lead to feelings of loneliness and further exacerbate anxiety and depression. Over time, the lack of social support and interaction can create a sense of disconnection from others, making it more difficult to cope with the emotional impact of hair loss.
2. Impact on Intimacy:
For some, hair loss can negatively affect romantic relationships, particularly if one partner feels less attractive or less confident due to their changing appearance. This can lead to decreased intimacy, communication issues, and misunderstandings. Partners may struggle to understand the emotional impact of hair loss, leading to feelings of frustration or inadequacy on both sides.
Coping Strategies for Emotional Resilience
While hair loss can be emotionally challenging, there are several strategies that can help individuals cope with its impact. Building emotional resilience is key to maintaining mental health and well-being in the face of hair loss.
1. Acceptance and Positive Self-Talk:
One of the first steps in coping with hair loss is learning to accept it as a part of life rather than a defining feature. This can involve reframing how you view hair and beauty, recognizing that self-worth is not tied to physical appearance. Practicing positive self-talk and affirmations can help shift focus away from the loss and toward other aspects of yourself that you value, such as your personality, talents, and accomplishments.
2. Seeking Professional Help:
If hair loss is causing significant emotional distress, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. Therapists and counselors can provide support in processing emotions, developing coping strategies, and addressing any underlying mental health issues such as anxiety or depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), for example, can be effective in challenging negative thoughts and behaviors related to hair loss.
3. Joining Support Groups:
Connecting with others who are experiencing similar challenges can be incredibly therapeutic. Support groups, whether in-person or online, offer a safe space to share experiences, exchange advice, and receive encouragement from others who understand what you’re going through. These groups can also provide valuable information about treatments, products, and strategies for managing hair loss.
4. Exploring Hair Alternatives:
For those who find it difficult to cope with the visual impact of hair loss, exploring hair alternatives such as wigs, hairpieces, or hats can be a helpful way to regain a sense of control and confidence. There are many high-quality options available today that look natural and can be styled to suit your preferences. Additionally, some individuals find creative ways to embrace their new look, whether through bold fashion choices or by adopting a different hairstyle that works with thinning hair.
5. Focusing on Overall Well-Being:
Maintaining a focus on overall health and well-being can also improve how you feel about your appearance. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can enhance your mood, reduce stress, and contribute to a positive outlook. Engaging in activities that make you feel good, such as hobbies, socializing, or volunteer work, can also shift attention away from hair loss and toward what truly matters in your life.
When to Consult a Dermatologist
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, and while some shedding is a normal part of the hair growth cycle, there are times when it becomes crucial to seek professional help. Consulting a dermatologist can be the key to understanding the underlying causes of your hair loss and finding the most effective treatment options. In this section, we will explore when you should consider making an appointment with a dermatologist and what to expect during the consultation.
Recognizing the Signs That Require Professional Attention
1. Sudden or Rapid Hair Loss:
If you notice that you are losing hair suddenly or in large amounts, it’s important to see a dermatologist as soon as possible. Sudden hair loss can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as an autoimmune disorder, thyroid disease, or even an infection. A dermatologist can perform the necessary tests to diagnose the cause and begin appropriate treatment.
2. Patchy Hair Loss:
Experiencing hair loss in small, circular patches can be indicative of conditions like alopecia areata, where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles. This type of hair loss is often unpredictable and can spread to other parts of the scalp or body. Early diagnosis and intervention by a dermatologist can help manage the condition and potentially reverse the hair loss.
3. Thinning Hair or Widening Part:
Gradual thinning of hair, particularly at the crown or along the part line, may be a sign of androgenic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness). This is the most common form of hair loss and is often hereditary. While it progresses slowly, early intervention with treatments such as Minoxidil or Finasteride can slow down the process and help preserve your hair.
4. Scalp Issues Accompanying Hair Loss:
If your hair loss is accompanied by other scalp issues, such as itching, redness, scaling, or pain, it could indicate a scalp infection or skin condition like psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis. These conditions can lead to further hair loss if left untreated, so it’s important to consult a dermatologist who can prescribe the appropriate treatment.
5. Hair Loss After a Medical Event:
If your hair loss began after a significant medical event, such as surgery, childbirth, or a major illness, it could be a form of telogen effluvium, a temporary condition caused by physical or emotional stress. A dermatologist can help determine if this is the case and recommend ways to support hair regrowth.
What to Expect During Your Dermatologist Visit
When you visit a dermatologist for hair loss, they will begin by taking a detailed medical history and asking about your hair care routine, diet, stress levels, and any family history of hair loss. They may also perform a scalp examination to look for signs of inflammation, scaling, or other abnormalities.
In some cases, the dermatologist may order blood tests to check for underlying conditions, such as thyroid dysfunction or nutritional deficiencies, that could be contributing to your hair loss. A scalp biopsy, where a small sample of scalp tissue is taken for examination, might also be performed to provide a more accurate diagnosis.
Once the dermatologist has determined the cause of your hair loss, they will discuss the available treatment options with you. This may include topical or oral medications, lifestyle changes, or even advanced procedures like PRP therapy or hair transplants, depending on the severity of the condition.
Conclusion
Hair loss is a multifaceted issue that affects not only physical appearance but also emotional well-being and self-confidence. Understanding the various causes of hair loss—whether genetic, hormonal, or due to lifestyle factors—is the first step toward addressing this common concern. While hair loss can be distressing, it’s important to remember that there are numerous treatments and lifestyle changes available that can help manage or even reverse the condition.
From over-the-counter medications like Minoxidil and prescription treatments such as Finasteride to more advanced options like PRP therapy and hair transplants, there are effective solutions tailored to different types and stages of hair loss. Additionally, incorporating a balanced diet, managing stress, and adopting gentle hair care practices can significantly contribute to maintaining healthy hair.
Equally important is recognizing when to seek professional help. Consulting a dermatologist early can lead to a proper diagnosis and more successful treatment outcomes. Whether you’re experiencing sudden hair loss, thinning hair, or scalp issues, a dermatologist can provide the expertise needed to navigate the complexities of hair loss.
In conclusion, while hair loss can be challenging, a proactive approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and professional guidance offers the best chance for preserving and restoring your hair health. By taking action early and exploring all available options, you can regain control over your hair and, more importantly, your confidence.
If you’re struggling with hair loss and want to take proactive steps to address it, don’t wait any longer. Explore the comprehensive resources available on our blog to learn more about effective treatments, lifestyle changes, and expert advice tailored to your needs. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular updates, tips, and the latest research in hair care and health. Share your experiences and questions in the comments section—we’re here to support you on your journey to healthier, stronger hair. Take control of your hair health today and start your path to renewed confidence!